
There is an area in the brain known as the internal capsule, and the symptoms that are brought on by a stroke that damages the internal capsule are very specific.
The term “internal capsule” is used to refer to a part of the brain that is located deep within the organ and serves as a communication conduit. Communication is possible between different parts of the cerebral cortex and different parts of the brainstem because of the internal capsule. These linkages are required for both the actual movement of the body as well as the perception of sensory information. They are made possible by the pathways of the internal capsule.
The role of the relay station in the body’s motor function is the most important one that the internal capsule plays in the body. This demonstrates that the internal capsule is essential for the movement of the arms, legs, trunk, and face. The internal capsule’s right side is responsible for transmitting nerve signals that control movement on the left side of the body, whereas the internal capsule’s left side is responsible for transmitting nerve signals that control movement on the right side of the body.
Although its primary function is to facilitate movement, the internal capsule also performs the function of a relay station, transmitting sensation from one side of the body to the other. Because it appears white when viewed through a microscope, the anterior capsule is sometimes referred to as “white matter.”
The weakness that results from an internal capsule stroke is referred to as hemiparesis or hemiplegia and might affect the arms, hands, legs, or feet. It’s possible that the damaged side of your body will retain some strength (hemiparesis), but it’s also possible that you won’t be able to move it at all (hemiplegia.) Because a stroke in the internal capsule can also affect the action of the muscles of the face, it may become difficult to chew food, swallow, or speak clearly after suffering one.
A stroke that affects the internal capsule, which is a pathway connecting nerves that govern both your sensation and your motor function, might cause you to lose some or all of your senses in the affected arm, leg, or face.
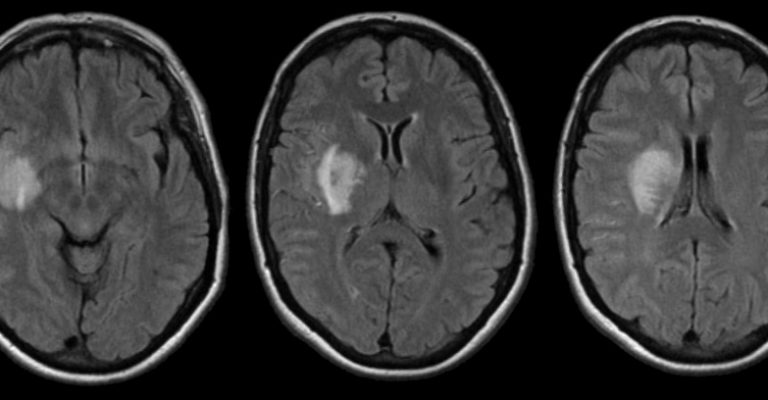
A seemingly little stroke in the internal capsule can cause severe weakening or loss of sensory perception due to the fact that so many essential pathways go via the internal capsule.
This occurs within a short period of time following the stroke. However, because the strokes that occur in the internal capsule are so minute, there are times when they are not clearly apparent in brain imaging scans, despite the fact that they induce severe symptoms.
A disruption in blood supply in the MCA or one of its tiny branches is the root cause of an internal capsule stroke. An embolic blood clot can induce an ischemic internal capsule stroke if it travels from one part of the body to another and then blocks one of the smaller branches of the middle cerebral artery (MCA). A stroke that occurs in this region is known as a lacune stroke or a lacunar stroke.
In addition, it is possible that the condition was brought on by the formation of a thrombotic blood clot within one of the tiny arteries that feed oxygen-rich blood to the internal capsule. After years of exposure to risk factors for stroke, a person may eventually acquire a cerebrovascular illness or heart disease, either of which can lead to a thrombotic or embolic stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke can also affect the internal capsule, and it is possible that the same risk factors that can induce an ischemic stroke might also cause a hemorrhagic stroke. These risk factors include hypertension and smoking.
The vast majority of patients who suffer from internal capsule strokes survive their injuries, and the vast majority of those who do survive have some degree of recovery. Strokes that occur in the internal capsule do not typically result in the significant swelling or convulsions that are typically associated with strokes that occur in other parts of the brain.
You may continue to feel weakness on one side of your body after having an internal capsule stroke. However, with physical therapy and stroke rehabilitation, you will likely experience some degree of improvement, although recovery is diverse from one stroke survivor to the next.
After a stroke affecting the internal capsule, it is common practice for the patient to have a medical evaluation to see whether or not they have any stroke risk factors. If this evaluation finds that you have risk factors for stroke, such as smoking, heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, or a blood problem, you need to make adjustments to your lifestyle or begin taking new drugs.

Rehabilitating someone who has had an internal capsule stroke calls for a specialized, individualized strategy that is tailored to the patient in question and their particular set of difficulties. Stroke survivors can benefit from participating in rehabilitation therapies because it can help them determine which functions need to be improved and teach them appropriate exercises or activities that can assist improve those functions.
Individuals who have had an internal capsule stroke may benefit from rehabilitation techniques such as the following: