
Stroke survivors can recover fully if they receive timely medical attention and participate in an appropriate stroke rehabilitation program.
However, some people may develop long-term motor deficits due to a stroke. An ischaemic stroke is a type of cerebrovascular accident that affects the pons region of the brain stem. It is also known as a pontine cerebrovascular accident (sometimes called a pontine CVA or pontine stroke).
A pontine stroke can be life-threatening and may result in paralysis and the rare syndrome known as Locked-In Syndrome (LiS).
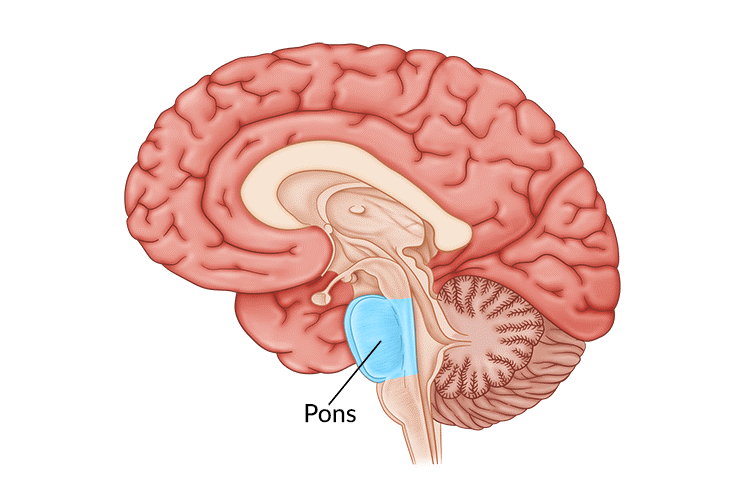
The brain stem is the location of around 10 percent of all ischemic strokes. A pontine cerebral vasculature stroke affects the pons region of the brain stem; nevertheless, a brief anatomy lesson is needed to comprehend the function of the brain entirely stem and the structure of the pons.
The brain stem is located along the bottom of the brain, between the spinal cord and the two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex. It is responsible for controlling the functions of the central nervous system (CNS).
The midbrain, the medulla oblongata, often known as the myelencephalon, and the pons are the three parts that make up the brain stem (metencephalon). Each of these is in charge of a distinct group of operational aspects.
The brain stem controls a wide variety of vital life activities, including breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and swallowing, amongst others. So, what are the negative consequences of having a stroke in the pontine region? Let’s have a look.
Stroke affecting the brainstem leads to a significant decline in motor function and other impairments. The specific symptoms that a patient experiences will be determined not just by the severity of the pontine stroke. It is also by the location of the stroke itself.
This is because cranial nerves perform various activities in various regions of the brain stem and inside the pons itself. Ataxia, for instance, is a condition in which a person’s muscles lose their ability to coordinate with one another. A stroke on the rear of the pons can cause this. In addition to double vision, vertigo, and dizziness are other common symptoms of a pontine stroke.
Some people may experience difficulty eating, speech problems and numbness after a pontine stroke. This type of stroke can result in a rare neurological condition called Locked-In Syndrome (LiS).
Patients with LiS have cognitive and vital functions similar to what they had before the stroke but have total or near-total physical paralysis. Most people diagnosed with LiS have some degree of eye movement control, provided their midbrains have not been damaged.
Many stroke survivors may start a specific rehabilitation program to rectify the impairments caused by the stroke. This program may include medication and physical and occupational therapy to help restore motor functions.
To make up for these shortcomings, the affected individual could also require alterations to their place of residence and their wardrobe.
In addition, occupational therapy will assist patients in regaining basic abilities that may have been lost due to impairments brought on by the stroke. Some examples of these skills include getting dressed and preparing meals. Rehabilitation following a stroke will start as soon as possible, within just a few days, for medically stable individuals.
Although these treatment programs may assist many people who have survived a stroke to make a satisfactory recovery. Because of this, the best treatment is prevention.
Thankfully, individuals can take various simple steps to lower their chance of suffering a pontine stroke in the future.
Strokes are the most significant cause of long-term disability in the United States. Each year, almost 800,000 people in the United States are affected by this condition.
People can significantly lower their stroke risk by making several relatively simple improvements to their lifestyle.
The likelihood of an individual having a stroke in their lifetime is nearly multiplied by four when they have hypertension.
On the other hand, lowering high blood pressure can be accomplished by maintaining a nutritious diet.
It is possible to lower blood pressure effectively and, as a result, an individual’s risk of stroke by reducing the amount of salt consumed. It is also advisable to increase the number of fruits and vegetables consumed daily, and avoiding foods high in cholesterol.
The Stroke Association estimates that maintaining a regular exercise program can reduce the risk of stroke by as much as 27 percent.
It is essential to strive for a daily caloric intake that ranges between 1,500 and 2,000 calories. This depends on a person’s activity level and body mass index, to facilitate the loss of weight in a manner that is both healthy and safe.
Individuals should also make it a priority to reduce the amount of alcohol they consume and kick any other unhealthy habits. They engage in because both of these factors contribute to an elevated risk of stroke.
Conditions like high blood pressure that have not responded to changes in diet and exercise may require medical intervention.