Brown-Séquard Syndrome (BSS) is a rare neurological disorder that affects the spinal cord. It is named after Charles-Édouard Brown-Séquard, the French physician who first described it in 1850. BSS can happen due to various reasons, such as tumors, spinal cord injuries, or infections.
The condition affects the nerve tracts that transmit signals between the brain and the body. As a result, individuals with BSS may experience a range of symptoms, including paralysis, numbness, muscle weakness, and difficulties controlling movement and sensation on one side of the body.
This blog post will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Brown-Séquard Syndrome. We’ll discuss different strategies to help manage the condition and improve the quality of life for those affected. If you or someone you know has BSS or is experiencing similar symptoms, this post will provide valuable information on how to cope with this rare disorder.
What is Brown-Séquard Syndrome?
Brown-Séquard syndrome (BSS) is an uncommon neurological condition that can cause muscle weakness or paralysis on one side of your body and a loss of sensation on the opposite side. This happens when there is damage to your spinal cord in a specific area on one side only.
Your spinal cord is a vital part of your nervous system that runs through the center of your spine from your brain to your lower back. Its delicate structure contains numerous nerve bundles and cells responsible for transmitting messages to and from your brain throughout your entire body.
When BSS occurs, it can affect your motor skills and physical movements. You may experience difficulties with balance and coordination and a loss of strength or control on one side of your body. Additionally, your sensation may be compromised, making it difficult to feel touch, heat, or cold on the opposite side of the damaged area.
It’s a type of spinal cord injury that’s considered incomplete. This means there is some sensory and/or motor function preservation below the area of the spinal cord where the injury occurred. On the other hand, a complete spinal cord injury results in the loss of all sensory and voluntary motor functions below the injury site.
People with Brown-Séquard Syndrome may experience a variety of symptoms, depending on where the injury occurred. For example, if the injury is on one side of the spinal cord, the person may have weakness or paralysis on that side but still retain some sensation. They may also experience pain, tingling, or other abnormal sensations.
What is the Difference Between Central Cord Syndrome and Brown-Séquard Syndrome?
Central cord syndrome (CCS) and Brown-Séquard syndrome (BSS) are both types of spinal cord injuries. CCS happens when there’s an incomplete injury in the center of the spinal cord, often in the neck area.
CCS causes weakness in the arms, which is more severe than in the legs. On the other hand, BSS is a condition that results from an incomplete injury that can occur anywhere along the spine. BSS causes weakness or paralysis on one side of the body and a loss of sensation on the other side below the injury site.
Spinal cord injuries are devastating for those who suffer from them. Both CCS and BSS can cause significant, long-lasting damage. CCS is most commonly observed in older individuals, while BSS often affects younger populations. It’s worth noting that both types of injuries can happen to anyone at any age.
Causes of Brown-Séquard Syndrome
Here are some of the causes of Brown-Séquard Syndrome.
Spinal Cord Injury
The primary cause of Brown-Séquard Syndrome is trauma to the spinal cord. This trauma often results from injuries such as car accidents, falls, or sports-related incidents.
The spinal cord, a delicate bundle of nerves encased in the spine, gets damaged when subjected to sudden and forceful impact. The severity of the injury and the specific location along the spinal cord determine the extent and nature of the symptoms associated with Brown-Séquard Syndrome.
Penetrating Injuries
Penetrating injuries, though less common, can be a significant trigger for Brown-Séquard Syndrome. These injuries occur when an object pierces through the spinal cord, causing damage to one side while leaving the other side relatively unaffected. This asymmetrical trauma results in the distinct sensory and motor deficits characteristic of Brown-Séquard Syndrome.
Tumors and Lesions
Tumors or lesions growing within the spinal cord can also lead to Brown-Séquard Syndrome. These abnormal growths exert pressure on the spinal cord or disrupt its normal functioning, creating an environment conducive to manifesting the syndrome’s symptoms. The impact varies depending on the tumor or lesion’s size, location, and nature.
Infections and Inflammatory Conditions
Infections affecting the spinal cord, such as abscesses or viral inflammation, can contribute to the development of Brown-Séquard Syndrome. Inflammatory conditions can also be underlying culprits, including transverse myelitis, where the spinal cord becomes inflamed.
These conditions disrupt the normal transmission of signals along the spinal cord, leading to the characteristic motor and sensory impairments associated with Brown-Séquard Syndrome.
Degenerative Disorders
While less common, certain degenerative disorders can play a role in the onset of Brown-Séquard Syndrome. Conditions like multiple sclerosis or degenerative disc disease can gradually affect the spinal cord’s integrity, leading to a cascade of symptoms resembling those seen in Brown-Séquard Syndrome. The gradual nature of these disorders may result in a slower onset of symptoms compared to acute traumatic causes.
Iatrogenic Factors
In some cases, medical interventions or procedures may unintentionally lead to Brown-Séquard Syndrome. Surgical procedures involving the spinal cord or nearby structures carry inherent risks. A poorly executed surgery or complications arising during the procedure can result in damage to the spinal cord, triggering the symptoms of Brown-Séquard Syndrome.

Treatment Options for Brown-Séquard Syndrome
Brown-Séquard Syndrome, characterized by a unique combination of motor and sensory impairments, requires a thoughtful and comprehensive approach to treatment.
Immediate Medical Care
The journey towards recovery from Brown-Séquard Syndrome often begins with immediate medical care, especially in cases resulting from traumatic injuries. Swift intervention is crucial to address trauma, prevent further damage, and stabilize the individual.
Emergency measures may include immobilizing the spine, administering medications to reduce inflammation, and addressing potential shock. This initial phase sets the foundation for subsequent treatment strategies.
Surgery
In cases where Brown-Séquard Syndrome stems from spinal cord compression due to tumors, lesions, or certain degenerative conditions, surgery becomes a pivotal treatment option. The aim is to repair the damage, alleviate pressure on the spinal cord, and create an environment conducive to healing. Surgical procedures may involve removing tumors, repairing herniated discs, or addressing other structural issues contributing to the syndrome.
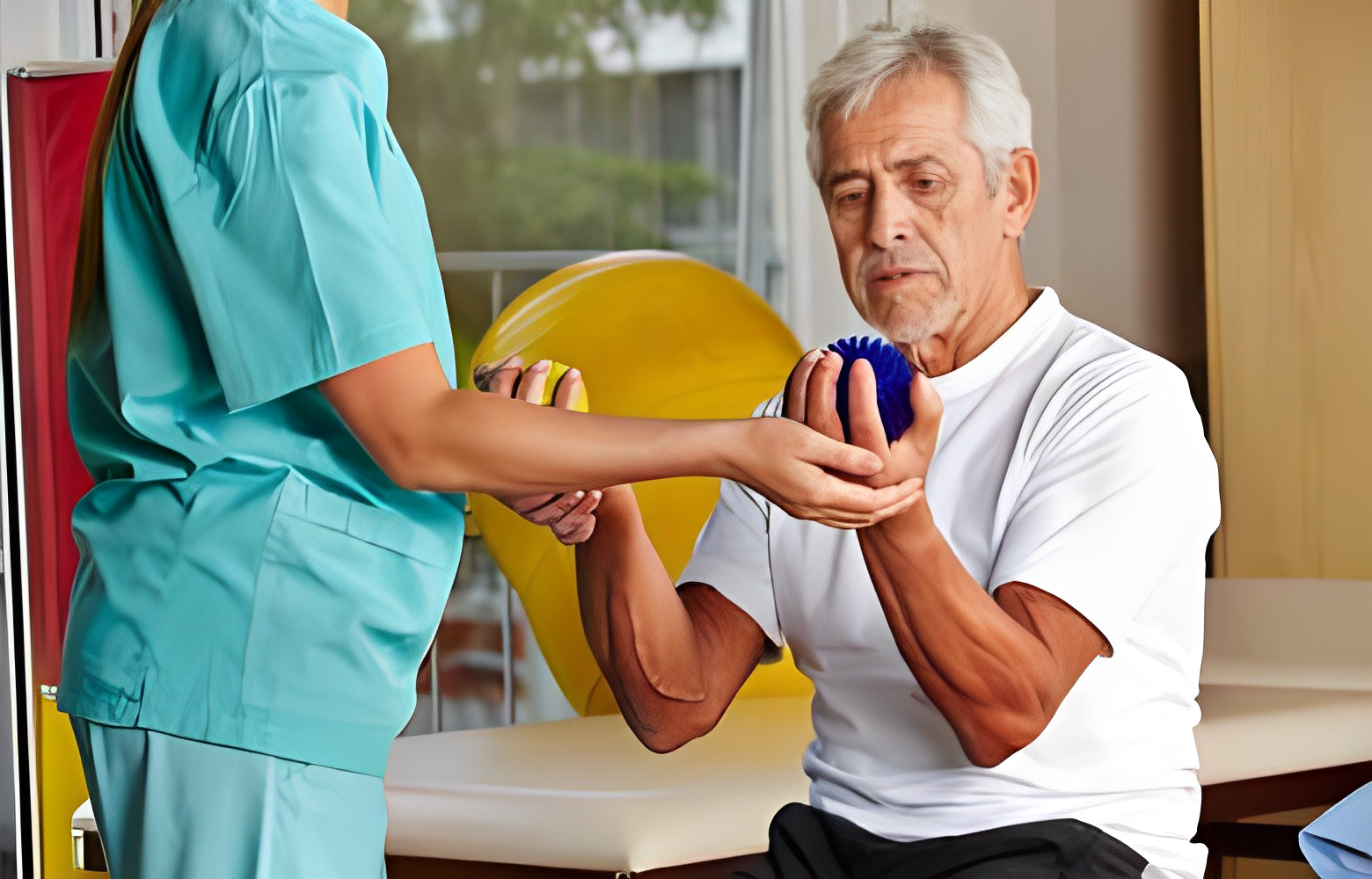
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a central role in the rehabilitation process for individuals affected by Brown-Séquard Syndrome. Skilled physical therapists work closely with patients to design tailored exercise regimens to improve mobility, strength, and coordination.
The focus is on regaining functionality and adapting to the unique challenges posed by the syndrome. Rehabilitation exercises may include targeted strength training, balance exercises, and activities to enhance fine motor skills.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapists collaborate with patients to develop strategies for overcoming specific challenges Brown-Séquard Syndrome poses. This may involve adaptive techniques, the use of assistive devices, and training in activities of daily living. The goal is to empower individuals to regain independence and actively participate in their daily routines.
Medications
Medications play a crucial role in managing symptoms and addressing underlying conditions contributing to Brown-Séquard Syndrome. Pain management is often a key component, with analgesic medications prescribed to alleviate discomfort associated with nerve damage.
Anti-inflammatory drugs may reduce swelling, especially in cases involving spinal cord compression. Medications targeting specific underlying conditions, such as infections or inflammatory disorders, may be prescribed as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Long-Term Rehabilitation
Brown-Séquard Syndrome necessitates a long-term commitment to rehabilitation and adaptation. Long-term rehabilitation encompasses ongoing physical and occupational therapy, providing individuals with the tools and strategies to adapt to new realities. The focus shifts towards optimizing independence, enhancing quality of life, and supporting individuals in navigating the unique challenges posed by the syndrome.
A Holistic Approach to Recovery
The treatment journey for Brown-Séquard Syndrome involves:
- A multidimensional approach.
- Addressing immediate medical concerns.
- Repairing damage through surgery.
- Leveraging rehabilitation strategies for long-term recovery.
Physical and occupational therapy play pivotal roles in restoring functionality and enhancing daily living, while medications manage symptoms and underlying conditions.