As we move through our daily lives, we often take for granted the incredible power and complexity of the human body. With a simple thought, we can move our limbs, grasp objects, and communicate with those around us. However, sometimes our body’s natural functions can become compromised due to nerve and muscle damage, resulting in debilitating conditions such as spastic and flaccid paralysis.
These conditions can cause a wide range of symptoms, from involuntary muscle spasms and stiffness to weakness and even total loss of muscle control. But what exactly causes these conditions, and what can be done to help those who suffer from them?
We’ll explore the root causes of spastic and flaccid paralysis, as well as the latest treatments and therapies available to help individuals regain control over their bodies.
Function of the Nervous System in Regulating Muscle Activity
The nervous system is a complex network that helps us carry out our daily activities. It is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The CNS comprises the brain and spinal cord and is responsible for important functions such as planning, coordinating, and organizing our activities. It controls almost everything we do, from breathing to walking and even thinking.
The PNS stems from the spinal cord and connects the CNS to other body parts. It carries signals to and from the brain, making it possible to move our muscles and sense the world around us. This way, it acts as a communication line between the brain and the rest of the body.
Motor neurons, special cells in the PNS, are crucial to this process. They help carry signals that control muscle movement and create intricate circuits all over the body. These circuits signal voluntary and involuntary movements, such as breathing or heartbeat regulation.
With billions of neurons transmitting information at lightning speeds, the nervous system is a wonder of nature. Without it, we would be unable to feel, think, move, or simply survive.
Your body relies on a complex neural pathway to get your muscles moving. The process begins in your brain’s motor cortex, which sends signals to the upper motor neurons. These neurons then transmit the signals through your spinal cord to the lower motor neurons, which finally send the signals to the muscles throughout your body.
However, when any part of this pathway gets damaged, the result can be either spastic or flaccid paralysis. Spastic paralysis usually occurs when the upper motor neurons are damaged. This can cause muscles to be constantly stiff and make even basic movements a struggle.
On the other hand, if the lower motor neurons are damaged, the muscles can become weak, start twitching, or even atrophy. That can lead to flaccid paralysis, where muscle tone is lost, and the affected body part(s) cannot move.
Causes of Paralysis

Paralysis is a debilitating condition that can arise from various disorders affecting the nervous system. While the exact causes are varied, studies have narrowed them down to a few key culprits.
Stroke and spinal cord injury are among the most common reasons for paralysis, accounting for 33.7% and 27.3% of cases, respectively. However, other conditions can also cause paralysis, including multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, and traumatic brain injuries.
When someone experiences a stroke, areas of the brain responsible for motor function can become damaged. The brain’s hemispheres control movement on the opposite side of the body, so paralysis often occurs on either the right or left side of the body in the damaged part of the brain. This type of paralysis is referred to as hemiplegia and can be incredibly debilitating.
Paralysis can manifest in varying degrees of severity and associated symptoms, depending on the underlying cause. Even with intensive medical care, paralysis can have a profound effect on quality of life, independence, and daily functioning. This is why early identification and treatment of symptoms are critical to minimizing the long-term impact of paralysis.
Paralysis occurs when the spinal cord gets damaged, and nerves can no longer send signals to the brain. This can result in two types of paralysis – paraplegia or quadriplegia.
Paraplegia is when the lower limbs are paralyzed, while quadriplegia means paralysis in all four limbs. It’s important to note that the location and severity of the spinal cord injury or stroke can greatly affect the extent of the paralysis experienced by the survivor.
Moreover, survivors may experience different types of paralysis, such as spastic or flaccid paralysis. Spastic paralysis is characterized by muscle stiffness, while flaccid paralysis is a loss of muscle tone.

Understanding the Difference Between Spastic and Flaccid Paralysis
These are two neurological disorders that impact voluntary muscle movement. Despite falling under the broad umbrella of paralysis, they are pretty different. The primary distinction between the two lies in the muscle responses.
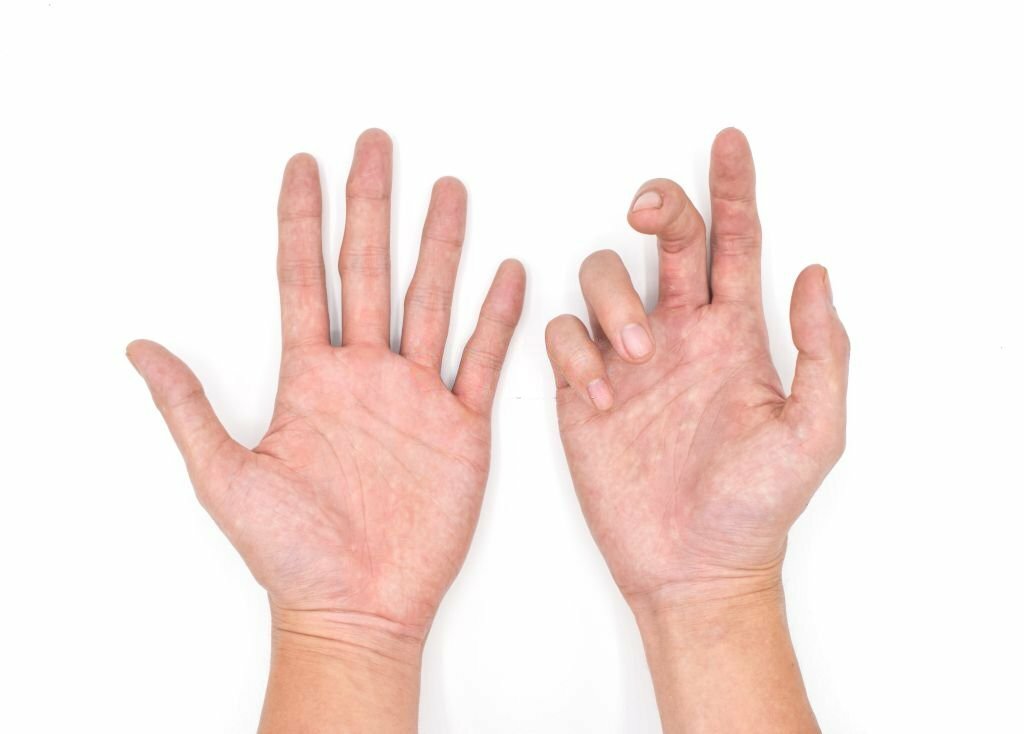
In spastic paralysis, the muscles are under constant contraction, which leads to stiffness and makes movement difficult. In contrast, in flaccid paralysis, the muscles cannot contract, resulting in a limp and weak appearance.
Although the root causes differ for each disorder, both lead to significant mobility issues for the affected individual. These difficulties can range from mild to severe, thereby making it crucial to diagnose the type of paralysis correctly to offer the appropriate treatment.
Flaccid Paralysis
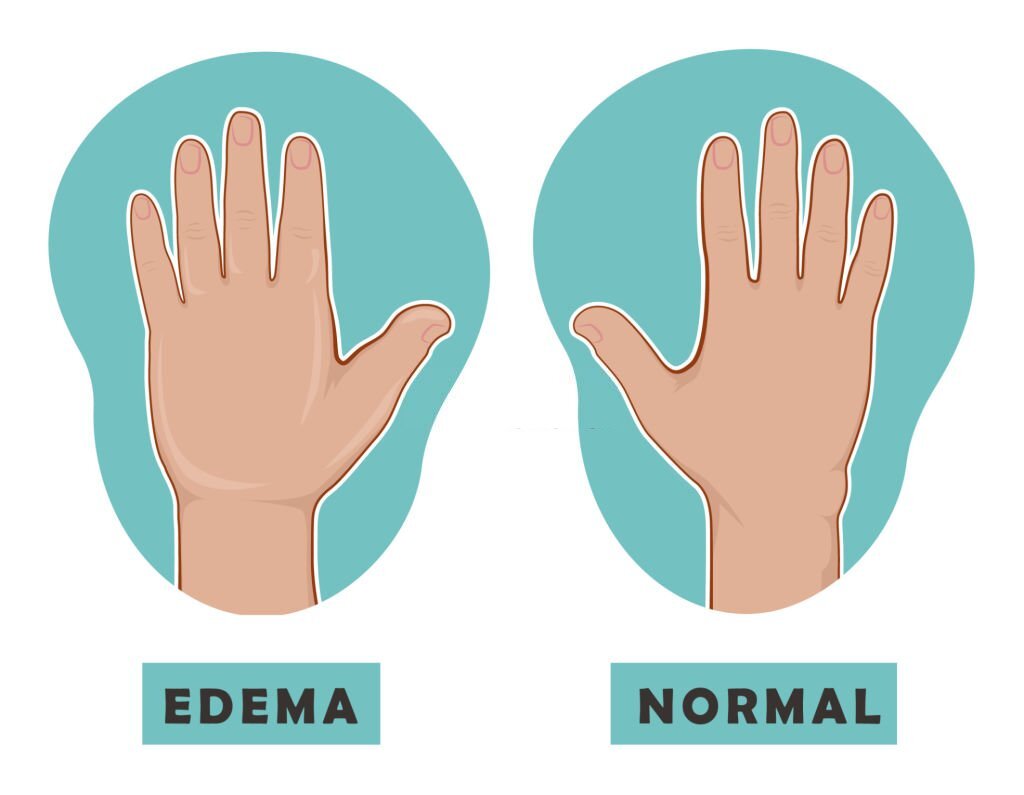
Flaccid paralysis is a serious condition that can cause a reduction in muscle tone. Muscle tone is the amount of muscle tension or resistance to movement. When this tone decreases, the muscles shrink and become loose or flabby. Limp muscles and a loss of muscle strength often characterize this condition.
This type of paralysis can occur due to various reasons, including viral infections, spinal cord injuries, and toxins. It affects people of all ages and can lead to a range of complications, including difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, and bladder and bowel problems.
Spastic Paralysis
It happens when the upper motor neurons become damaged, which leads to a loss of voluntary control over the affected muscles. This can be a tough situation for the affected individual, as their muscles respond to the imbalance of signals by becoming rigid and strained.
Moreover, muscle stiffness, spasms, and uncontrollable twitching are some of the signs that the person is suffering from spastic paralysis. In most cases, this type of paralysis affects the limbs, but it can also spread to other parts of the body. This can impact the person’s quality of life, making routine tasks such as walking, dressing, and eating a significant challenge.
Latest Treatments for Spastic and Flaccid Paralysis
Each type of paralysis requires a different approach to treatment, and medical professionals have been working hard to develop new treatments to improve patient outcomes.
Spastic Paralysis
Botulinum Toxin Injections
Botulinum toxin injections are a popular treatment for spasticity. These injections help to relax the muscles affected by spasticity, which can help with mobility and reduce pain. The effectiveness of botulinum toxin injections can vary depending on the severity of the spasticity, but it remains a popular treatment option for patients.
Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy
This relatively new treatment involves the continuous delivery of baclofen to the spinal cord. Baclofen is a muscle relaxant that can be highly effective in reducing spasticity. The treatment can be more targeted and effective by administering it directly to the spinal cord.
Electrical Stimulation Therapy
Electrical stimulation therapy involves using electrical currents to stimulate spasticity-related muscles. This therapy can help to reduce the stiffness and improve mobility in the affected area.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat spasticity. Surgical options can include cutting certain nerves or tendons to reduce the activity of the affected muscles. While surgery is generally considered a last resort, it can be highly effective in severe cases.
Flaccid Paralysis
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is often the first line of treatment for flaccid paralysis. It can help to improve strength, range of motion, and coordination in the affected area.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy involves the use of stem cells to repair damaged tissues and regenerate new ones. This therapy is still in the experimental stages, but early results have been promising for patients with flaccid paralysis.
Nerve Transfers
Nerve transfers involve taking functioning nerves from one part of the body and transferring them to the paralyzed area. This can help to restore function to the affected muscles and improve mobility in the affected area.
Final Thought
Medical professionals have been working tirelessly to develop new treatments for spastic and flaccid paralysis. Whether it’s through injections, electrical stimulation, or surgery, there are a number of treatment options available for patients suffering from these conditions. While some treatments are still in the experimental stages, early results have been promising, and there is hope that more effective therapies will be developed in the years to come.