What You Need to Know About a T6 Spinal Cord Injury

What if you woke up today and your life was completely changed? Just like that, all because of a spinal cord injury. It’s something that can happen to anyone at any time. But if you or someone you know is facing a T6 spinal cord injury, there are some important things you need to know.
Understanding the facts, the treatments, and the resources available to you can make all the difference in navigating this new reality. So, let’s dive in and discover what you need to know about a T6 spinal cord injury.
What is T6 Spinal Cord Injury?
T6 spinal cord injury is a form of paralysis that affects the entire lower body, including the chest, legs, and feet. It is caused by spinal cord damage, a bundle of nerves running down the back, transmitting signals between the brain and the body.
The T6 spinal cord injury usually occurs due to a severe blow or impact, such as a car accident, sports injury, or a fall. The person suffering from T6 spinal cord injury may become wheelchair-bound and require assistance with daily activities. The condition can also impact the bowel and bladder control and the blood pressure.
Complications of T6 Spinal Cord Injury
Spinal cord injury is a devastating condition that can impact a person’s life in countless ways. When the spinal cord is damaged at the T6 level or thoracic sixth vertebra, it can significantly impact a person’s function and independence.
Autonomic Dysreflexia
Autonomic dysreflexia is a potentially life-threatening complication that can occur in people who have a spinal cord injury above the T6 level. It is a reflex action that responds to a noxious stimulus, such as a bladder infection or pressure ulcer. The body responds with a surge in blood pressure that can cause a stroke or even death if left untreated.
People with T6 spinal cord injury are particularly vulnerable to autonomic dysreflexia because the nerves that control blood pressure and sweating below the level of damage are disrupted. Treatment involves identifying and treating the cause of the noxious stimulus, such as emptying the bladder or relieving pressure on a pressure ulcer and administering medication to lower blood pressure.
Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction
T6 spinal cord injury can also cause bladder and bowel dysfunction, which can be a significant source of discomfort and inconvenience for patients. The loss of control over the bladder and bowel can lead to urinary tract infections, constipation, and fecal incontinence, which can have a negative impact on a patient’s quality of life. Treatment options include catheterization, medications, and bowel management programs.
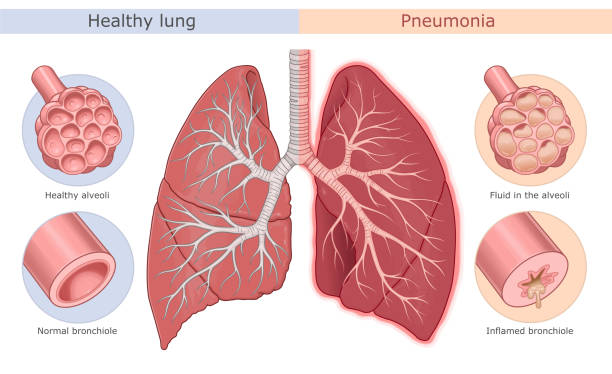
Pneumonia
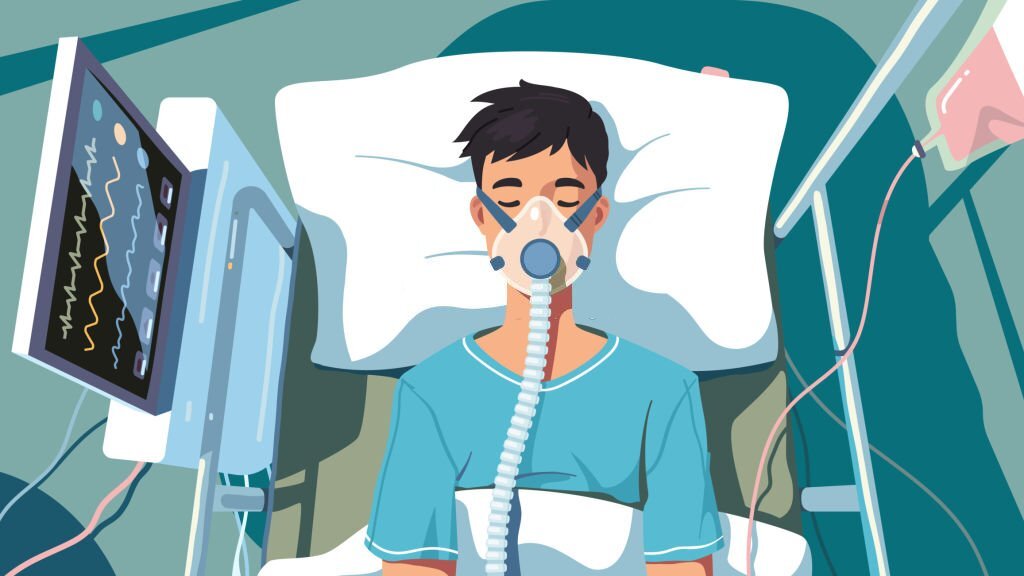
Pneumonia is a common complication in people with T6 spinal cord injury, as the paralysis of the diaphragm and chest muscles can make it difficult to breathe deeply and cough effectively. Patients with T6 spinal cord injury are at a higher risk of developing pneumonia due to weakened immune systems, impaired mobility, and lung function. Treatment involves antibiotics, breathing exercises, and chest physiotherapy.
Orthostatic Hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension is a sudden drop in blood pressure when a patient changes position from lying down to sitting or standing. This is because the body’s ability to regulate blood pressure is compromised in people with T6 spinal cord injury due to the autonomic nervous system disruption.
Orthostatic hypotension can cause dizziness, fainting, and falls, which can be dangerous for patients. Treatment involves medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes, such as avoiding sudden changes in position.
Poor Sitting Balance
T6 spinal cord injuries often damage the abdominal muscles, making it difficult to maintain an upright posture. A person with a spinal cord injury may become unbalanced and fall with as little as a slight tilt to one side.
Keep this in mind whenever you’re attempting to reach for anything (particularly if you’re using both hands)—if you extend too far, you could just fall out of your chair. Fortunately, normal hand and arm function persists even after a T6 spinal cord injury. Because of this, individuals can stand up straight using their arms and shoulders instead of their abs.
Spasticity
Spasticity is a common complication in people with T6 spinal cord injury, characterized by muscle stiffness that can cause pain, discomfort, and reduced mobility. It is caused by the hyperactivity of certain nerve pathways in the spinal cord that can lead to muscle contraction. Treatment options for spasticity include medications, physical therapy, and surgical procedures.
Pressure Sores
Pressure sores are a common complication in people with spinal cord injury, as the loss of sensation and mobility can lead to increased pressure on certain areas of the body, such as the buttocks, hips, and heels. If left untreated, pressure sores can lead to infection, sepsis, and even death. Treatment options for pressure sores include wound care, antibiotics, and surgery.
Managing T6 Spinal Cord Injury
The management of T6 spinal cord injury involves a multi-disciplinary approach. This includes addressing the patient’s physical, emotional, and social needs through a combination of medical interventions, rehabilitation, and support.
Medical Intervention
The medical management of T6 spinal cord injury involves stabilizing the patient’s condition and preventing complications. This includes close monitoring of the patient’s vital signs and respiratory and bladder function.
The patient may require mechanical ventilation to support breathing and medication to control blood pressure and prevent blood clots. Surgery may sometimes be necessary to stabilize the spine and address any other injuries.
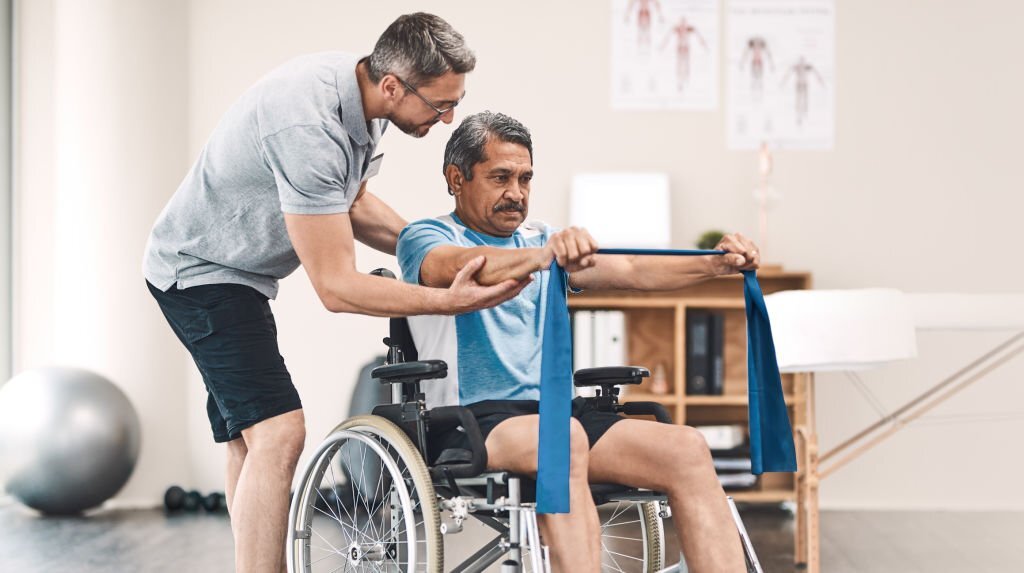
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the management of T6 spinal cord injury. It includes physical, occupational, and speech therapy to help the patient regain as much function as possible and adapt to new limitations.
Physical therapy focuses on strength training and mobility exercises to help the patient regain movement and balance. Occupational therapy helps the patient learn new skills and techniques for daily activities, such as dressing and cooking. Speech therapy is necessary if the patient has difficulty speaking or swallowing.
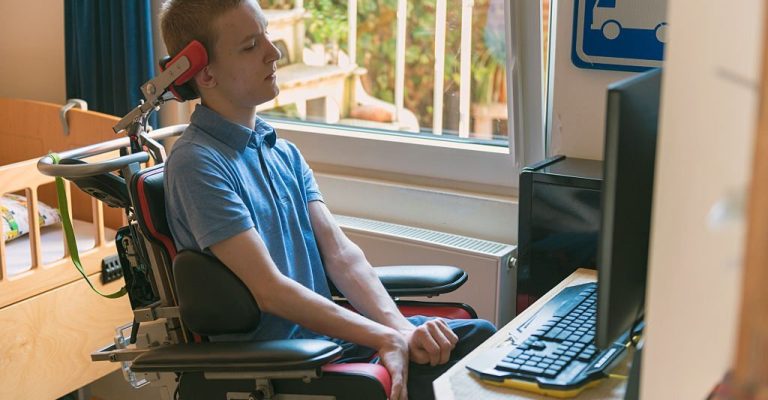
Assistive Technology
One of the most significant challenges for patients with T6 spinal cord injury is maintaining independence in their daily lives. Assistive technology can be extremely beneficial, and it is no exaggeration to say its impact can be life-changing.
Today’s technology can significantly enhance the quality of life of people with spinal cord injuries and other disabilities. Some of the assistive technology options that can be helpful for T6 spinal cord injury patients include:
Voice-activated Devices
Voice-activated devices such as Google Home or Amazon Alexa can be game-changers for people with T6 spinal cord injuries. These devices allow users to control their environment and access information hands-free without relying on their arms. They can handle everything from lights and thermostats to music and television shows.
Smart Home Devices
Smart home devices such as smart locks and cameras can increase security and allow more flexibility in daily routines. For example, smart locks can unlock the front door remotely or authorize access by caregivers or other visitors.
Adaptive Sports Equipment
Adaptive sports equipment can enable individuals with T6 spinal cord injuries to participate in recreational and competitive sports. These devices may include specialized wheelchairs, handcycles, or adaptive skiing and snowboarding equipment.
Support
Patients with T6 spinal cord injury require significant emotional and social support. They may experience depression, anxiety, or a sense of loss due to their condition. It is essential to provide them with counseling services and emotional support. Additionally, caregivers and family members also require support to effectively manage the patient’s needs.
To Sum Up
T6 spinal cord injury can significantly impact a person’s physical, emotional, and social well-being. It is essential to understand the specific complications and challenges of this type of injury to provide effective management and support for patients.
Through a combination of medical interventions, rehabilitation, and assistive technology, individuals with T6 spinal cord injury can regain some level of independence and improve their overall quality of life.